Submersible pumps rely on powerful motors to move large volumes of water, slurry, or industrial fluids. Since these motors operate fully submerged, effective sealing is critical to prevent fluid ingress, electrical damage, and premature motor failure.
Traditionally, mechanical seals have been used to protect submersible motors. In recent years, magnetically assisted or hermetically sealed motor designs, often referred to as magnetic sealing systems, have gained attention due to their advanced design and reduced wear.
Both sealing approaches have clear advantages and limitations. Understanding the differences helps engineers, buyers, and operators choose the right solution for their application.
Mechanical Seals: the Traditional Way of Sealing Submersible Motors
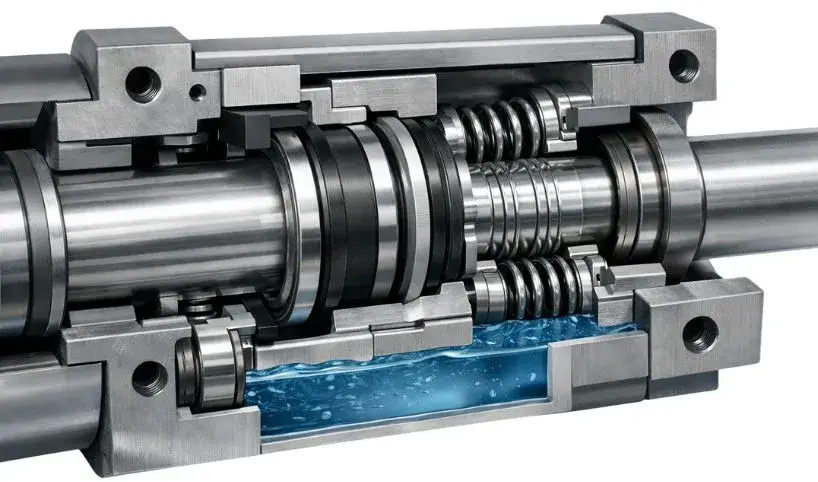
Mechanical seals have been used in submersible motors for decades and remain the most common sealing method. This system uses two flat sealing faces pressed together, one stationary and one rotating, to create a physical barrier that prevents fluid from entering the motor.
Advantages of Mechanical Seals
- Proven reliability: Mechanical seals have a long track record across agriculture, construction, mining, and wastewater applications. Their simple design makes them dependable in environments where suspended solids and slurry are present.
- Cost effective solution: Motors with mechanical seals are generally more affordable than advanced sealed motor designs. Spare parts are widely available, and replacement costs are relatively low.
- Easy maintenance and servicing: Most technicians are familiar with installing and servicing mechanically sealed motors. Repairs can usually be carried out quickly without specialised tools or training.
- Wide application compatibility: Mechanical seals perform reliably across a broad range of temperatures, pressures, and fluid types, including wastewater and moderately abrasive liquids.
Limitations of Mechanical Seals
- Wear and tear over time: Because mechanical seals rely on physical contact, friction causes gradual wear. This can shorten seal life and increase maintenance frequency.
- Risk of leakage: As seal faces wear, leakage may develop, especially in abrasive or corrosive environments.
- Reduced lifespan in harsh conditions: Sand, grit, and corrosive chemicals can damage seal faces, accelerating failure in demanding applications.
- Energy loss due to friction: Continuous contact between seal faces generates heat and friction, which slightly reduces motor efficiency.
Magnetic Seals and Hermetically Sealed Motors: Advanced Sealing Technology
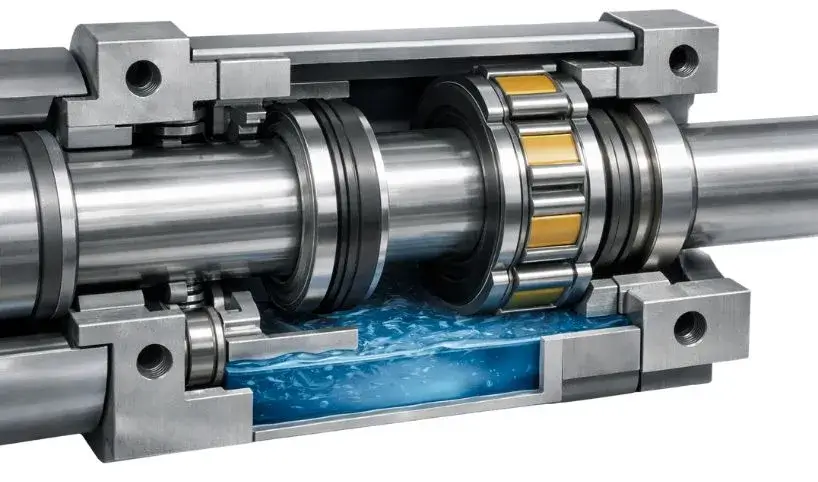

Magnetic sealing in submersible motors is commonly associated with hermetically sealed or magnetically coupled motor designs. In these systems, torque is transmitted using magnetic forces without a traditional rotating shaft penetrating the motor housing.
Instead of relying on direct physical contact, magnetic fields transfer rotational energy across a sealed barrier, eliminating dynamic shaft seals altogether.
Important Technical Clarification
In most industrial applications, magnetic systems do not replace mechanical seals in the traditional sense. Instead, they eliminate shaft penetration, creating a fully sealed motor chamber. This design significantly reduces leakage risk and mechanical wear.
Advantages of Magnetic or Hermetically Sealed Systems
- No physical contact at the seal point: The absence of rubbing seal faces greatly reduces wear and extends service life.
- Very low leakage risk: With no dynamic shaft seal, the chance of fluid ingress is minimal when operating within design limits.
- Excellent performance in abrasive and corrosive fluids: These systems are well suited for applications involving slurry, sand laden water, or aggressive chemicals.
- Higher energy efficiency: The elimination of friction at the sealing interface improves overall motor efficiency.
- Longer operational life and reduced maintenance: With fewer wear components, these motors typically require less frequent servicing.
Limitations of Magnetic Sealing Systems
- Higher initial cost: Advanced manufacturing and precision components make these motors more expensive upfront.
- Complex design and specialised servicing: Installation and repairs should be handled by trained technicians familiar with magnetically coupled systems.
- Temperature limitations: Magnetic materials can lose strength at high temperatures, making these systems unsuitable for extreme heat applications.
Mechanical Seal vs Magnetic Seal: Quick Comparison
| Feature | Mechanical Seal | Magnetic / Hermetic System |
|---|---|---|
| Physical contact | Yes | No |
| Wear and tear | Higher | Minimal |
| Leakage risk | Moderate over time | Very low |
| Maintenance | Regular | Minimal |
| Initial cost | Lower | Higher |
| Abrasive fluids | Limited suitability | Highly suitable |
| Energy efficiency | Slightly lower | Higher |
Which Seal Is Right for Your Application?
There is no universal answer. The right choice depends on operating conditions, budget, and performance expectations.
A mechanical seal is ideal when:
- Budget is limited
- Fluid is relatively clean
- Periodic maintenance is acceptable
- Simple and proven technology is preferred
A magnetic or hermetically sealed motor system is better when:
- Fluids contain abrasive solids or corrosive elements
- Downtime must be minimised
- Long service life is critical
- Higher initial investment is acceptable
At Unnati Pumps, sealing technologies are evaluated based on real operating conditions, fluid characteristics, and long term performance. This ensures customers receive submersible motor solutions that deliver reliability, efficiency, and durability for their specific application.


